Biologically active peptides are synthesized by different methods. The classical approaches to peptides production are called solution peptide synthesis and solid-phase peptide synthesis (SPPS). The solution approach is used for the synthesis of short peptides, such as di- and tripeptides, and C-terminally modified peptides, such as enzyme substrates. Stepwise condensation is based on the repetitive addition of single N-a-protected amino acids to a growing amino component, generally starting from the C-terminal amino acid of the chain to be synthesized. The process of coupling individual amino acids can be accomplished through employment of the carbodiimide, the mixed carbonic anhydride, or the N-carboxyanhydride methods. The controlled peptide synthesis requires selective protection and deprotection of the various functional groups: the amino group, the carboxyl group, or the side chain functional groups. The side group gives each amino acid its distinctive properties and helps to dictate the folding of the protein.
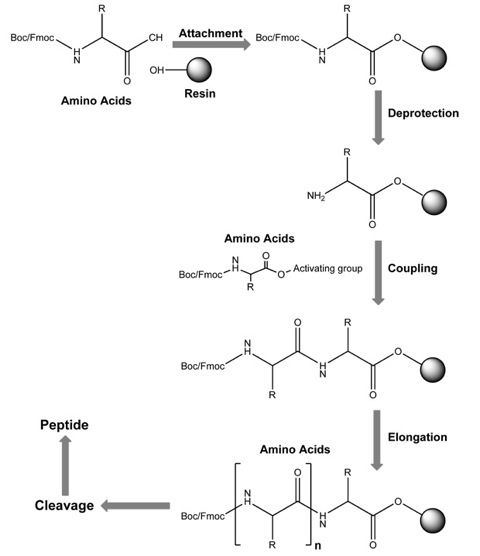
Solid Phase Peptide Synthesis (SPPS) technology - Fmoc/Boc Strategy
This technique immobilizes one end of the desired sequence onto a solid support matrix (Fmoc or Boc), and then incorporates N-a-amino acids into a peptide of any desired sequence. At the end of each coupling step, all soluble reagents can be removed from the peptide-solid support matrix by filtration and washed away. The peptide can be removed from the polymeric support after the desired sequence of amino acids has been obtained.
Polypeptide formation - Recombinant protein expression and refolding technology
Production of large peptides especially peptides longer than 100 amino acids is most efficiently achieved by recombinant expression in E. Coli, mammalian cells, or cell-free protein synthesis platform.
Disclaimer
Information on this website is summarized from published literatures for education purpose only. All molecular structures listed are for example purposes but not meant to be used as ingredients in cosmetic products.
For regulatory policy of each molecule and its use for cosmetic product, please refer to the released information of FDA or your local government. All information is provided for informational and marketing purposes only.
